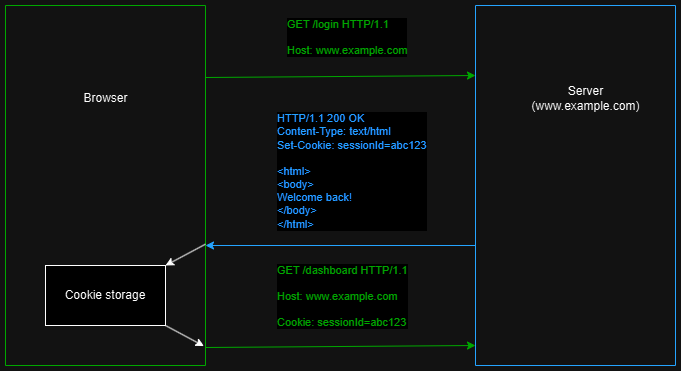
Cookies are just HTTP headers. However, special kind of headers which are used to keep information longer on a client side and then send it back to server. The basic flow is that a client asks for a resource, then a server responds with setCookie header and then the client stores given information and use it in all subsequent requests:
Set-Cookie header structure [server]
The basic structure of Set-Cookie goes like:
Set-Cookie: <cookie-name>=<cookie-value>; <attribute1>=<value1>; <attribute2>; ...So we can set only one key value pair and unlimited number of attributes (might be key value or only value). Every element separated by the semicolon For example:
Set-Cookie: sessionId=abc123; Path=/; HttpOnly; Secure; SameSite=StrictAvailable attributes
Path
Used to indicate to which response URL paths a cookie should be attached. So for the following one:
Path=/dashboardonly requests to /dashboard path and all underlying paths (like /dashboard/mobile) will have a cookie. To set a cookie for all possible paths, you use single slash:
Set-Cookie: sessionId=abc123; Path=/Domain
Says to which domain a cookie belongs to. So to limit a cookie to example.com domain you need to use:
Set-Cookie: sessionId=abc123; Domain:example.comExpires
As the name suggests, it lets a server to decide when a cookie will be removed (not send anymore). If not set, then a cookie is stored only during browser session (after closing a browser is it is removed).
Set-Cookie: userId=abc123; Expires=Tue, 19 Jan 2038 03:14:07 GMTMax-Age
The same purpose as Expires, but takes time in seconds instead of datetime.
Set-Cookie: userId=abc123; Max-Age=3600Secure
Ensures that a cookie is sent only via HTTPS:
Set-Cookie: userId=abc123; SecureHttpOnly
Ensures that a cookie can not be accessed by JavaScript code (for example using document.cookie):
Set-Cookie: userId=abc123; HttpOnlySameSite
Decides if a cookie is attached to subsequent requests when it comes to cross site requests (see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cross-site_request_forgery for more). Available options are:
– Strict (cookies are not attached while cross site requesting)
– Lax (cookies are attached only for GET and HEAD requests)
– None (cookies are attached to all cross site requests)
Usually by default (if not set) cookies are attached to all cross site requests.
What if I need to send more than one key value pair?
When it comes to sending more than one value, you need to send two Set-Cookie headers like:
Set-Cookie: sessionId=abc123; Max-Age=3600
Set-Cookie: userId=def456; Expires=Tue, 19 Jan 2038 03:14:07 GMTCookie header structure [client]
Client when sending cookies back, it merges them all into one (separating them by the semicolon) and sends them under Cookie header name. So for a server response:
Copy CodeCopiedUse a different BrowserSet-Cookie: sessionId=abc123; Max-Age=3600
Set-Cookie: userId=def456; Expires=Tue, 19 Jan 2038 03:14:07 GMTthe client sends back:
Cookie: sessionId=abc123;userId=def456